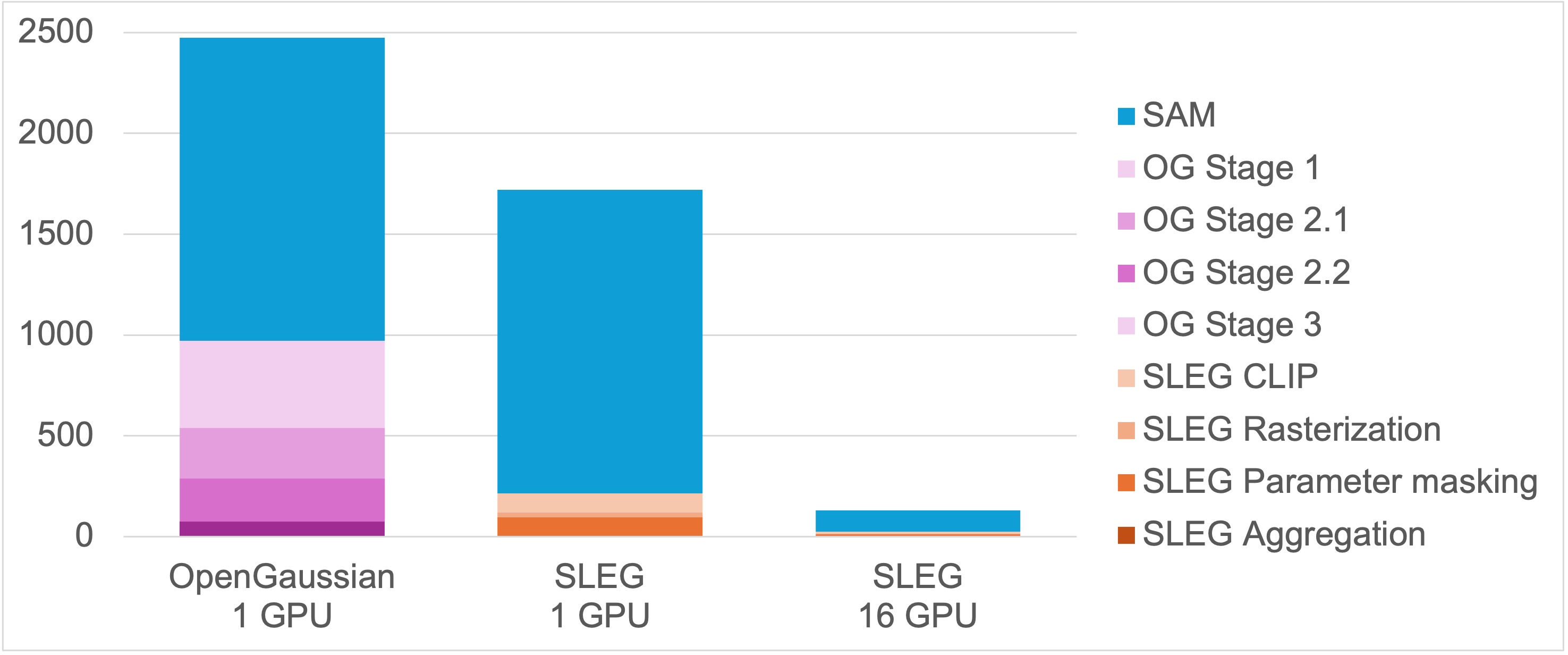
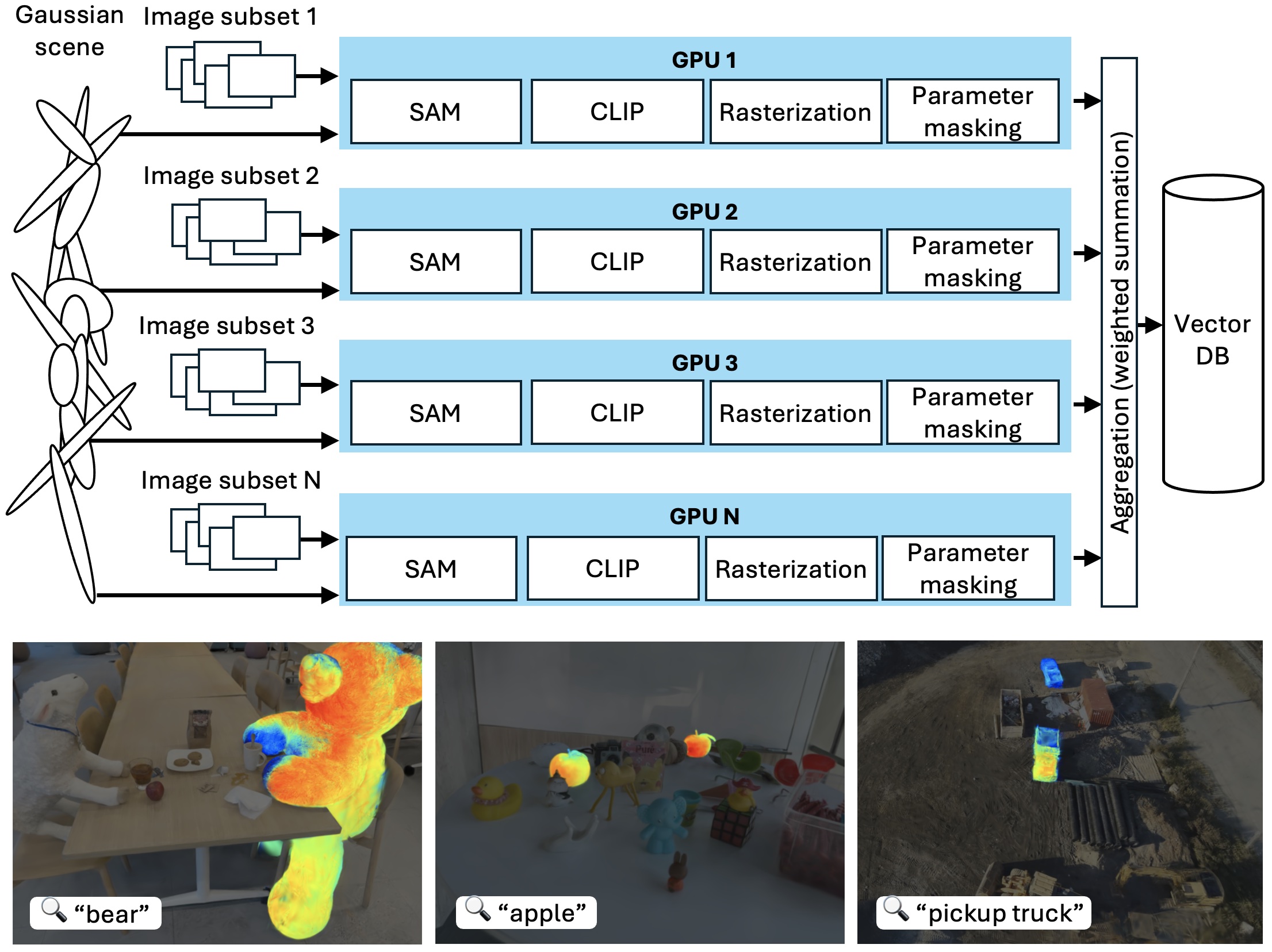
SLAG is a scalable method for augmenting large Gaussian splatting scenes with language features. Our method leverages multi-GPU parallelization to accelerate scene encoding and overcome the memory limitations of single-GPU systems.
Abstract
Language-augmented scene representations hold great promise for large-scale robotics applications such as search-and-rescue, smart cities, and mining. By enabling open-vocabulary natural language queries, language-augmented Gaussian splatting allows flexible retrieval of semantic information from large 3D scenes and integration with LLM agents. Many of these use cases are time-sensitive and data-intensive, demanding both rapid scene encoding and scalablility. Deploying such representationson for inference on robots with limited computational resources further compounds the challenge. To address this, we introduce SLAG—a multi-GPU framework for language-augmented Gaussian splatting that significantly improves the speed and scalability of language-augmenting large 3D Gaussian scenes.
Method Overview
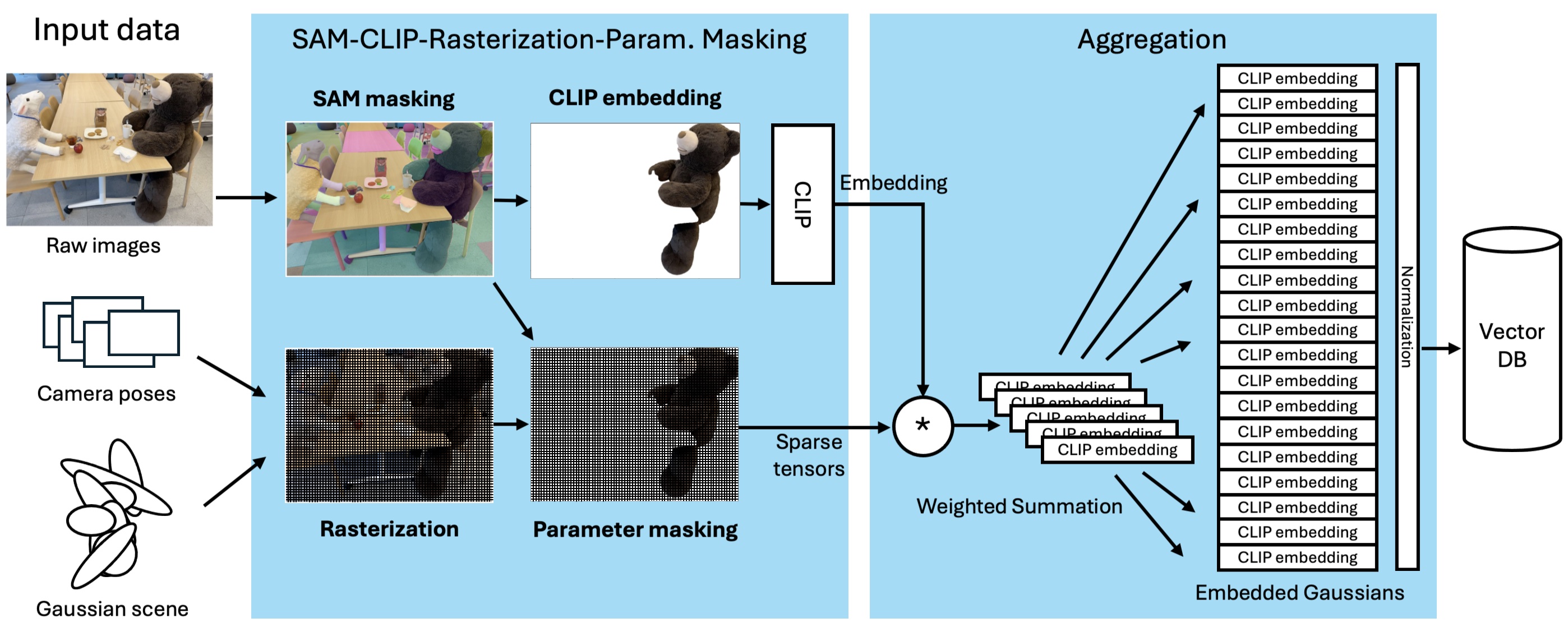
Our method integrates 2D visual-language model features into 3D scenes using SAM and CLIP. Unlike prior approaches, SLAG eliminates the need for a loss function to compute per-Gaussian language embeddings. Instead, it derives embeddings from 3D Gaussian scene parameters via a normalized weighted average, enabling highly parallelized scene encoding. Additionally, we introduce a vector database for efficient language embedding feature storage and inference retrieval. To further improve scalability, we introduce a vector database that stores language embeddings for fast and efficient querying at inference time.
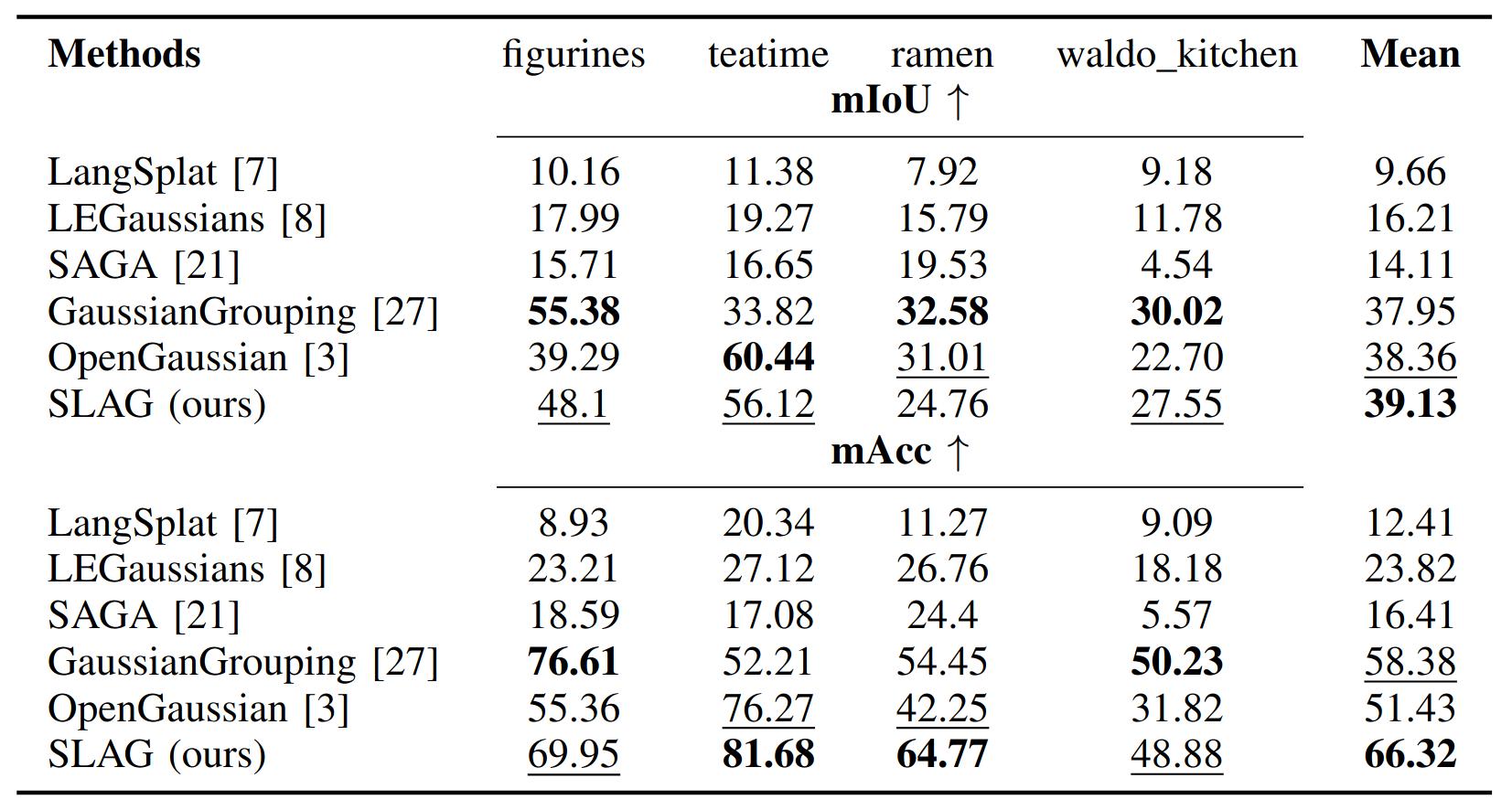
Quantitative Results
SLAG significantly accelerates scene encoding while maintaining state-of-the-art open-vocabulary segmentation performance. Our experiments demonstrate an 19× speedup in scene encoding on a 16-GPU setup compared to OpenGaussian, with no loss in embedding quality on the ScanNet and LERF datasets.